

· By Kelin Marquet
Sublingual B12 vs Injection
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of nerve cells, the formation of red blood cells, and DNA synthesis.
Unfortunately, B12 deficiency is not uncommon, and it can lead to fatigue, weakness, anemia, and neurological problems. To tackle this issue, individuals can choose between sublingual B12 supplementation and B12 injections. In this article, we'll delve into the pros and cons of each method, the most effective form of B12 for each, the dosages, and how long it takes for them to work.
B12 Deficiency: The Signs
A B12 deficiency can manifest in several ways, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Some common signs include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Anemia
- Pale or jaundiced skin
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet
- Difficulty maintaining balance
- Glossitis (a swollen, red, and inflamed tongue)
- Memory problems or cognitive decline
If you suspect a B12 deficiency, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Does Sublingual B12 Work?
If you're accustomed to getting your B12 from injections, you may be wondering what the research says. Good news: yes, B12 supplements really work.
In a large study of 4281 patients, serum B12 was compared between those receiving intramuscular injections and those on a sublingual methylcobalamin supplement. The results? The B12 levels were actually highest in those taking a supplement! (1)
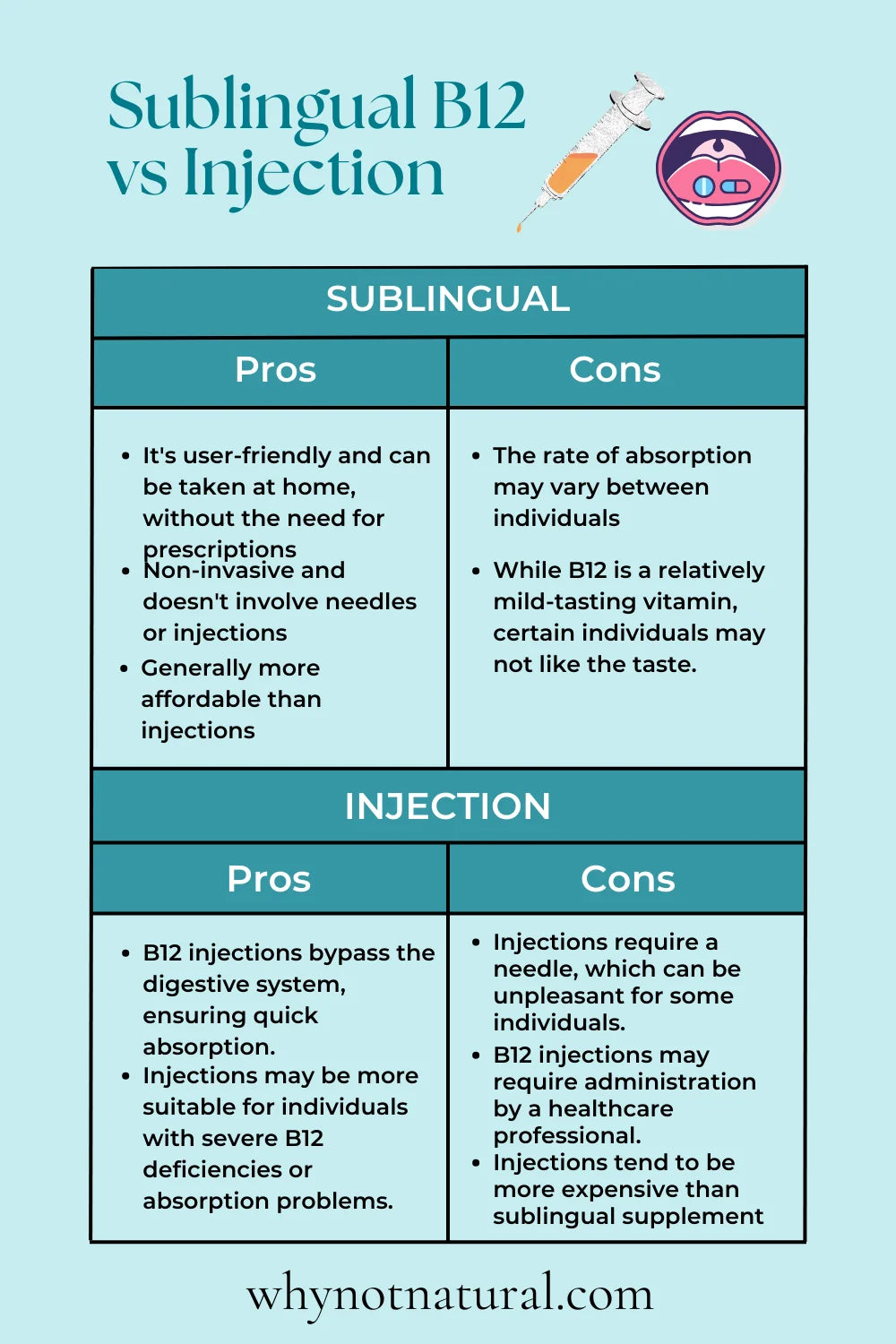
Sublingual B12 Supplementation: Pros and Cons
Sublingual B12 supplements are placed under the tongue, where they are absorbed into the bloodstream through the mucous membranes (sometimes compared to a secret "trap door" beneath the tongue). Let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of this method:
Pros:
- Easy to administer: Sublingual B12 supplements are user-friendly and can be taken at home, without the need for prescriptions.
- Less invasive: This method is non-invasive and doesn't involve needles or injections.
- Cost-effective: Sublingual B12 supplements are generally more affordable than injections.
Cons:
- Absorption variability: The rate of absorption may vary between individuals.
- Taste: While B12 is a relatively mild-tasting vitamin, certain individuals may not like the taste.
For sublingual supplementation, the most effective form of B12 is methylcobalamin, as it is readily absorbed and utilized by the body. A typical dosage ranges from 1,000 to 5,000 micrograms per day, depending on individual needs.
The absorption rate varies, but improvements in symptoms can often be observed within a week or two of starting supplementation.
B12 Injections: Pros and Cons
B12 injections involve the administration of the vitamin directly into the muscle, which allows for rapid absorption. Here are the pros and cons of this method:
Pros:
- Fast absorption: B12 injections bypass the digestive system, ensuring quick absorption.
- Effective for severe deficiencies: Injections may be more suitable for individuals with severe B12 deficiencies or absorption problems.
Cons:
- Invasive: Injections require a needle, which can be unpleasant for some individuals.
- Medical supervision: B12 injections may require administration by a healthcare professional.
- Higher cost: Injections tend to be more expensive than sublingual supplements and may not be covered by insurance.
For B12 injections, hydroxocobalamin or cyanocobalamin (a synthetic form of B12) are the most commonly used forms. The dosage and frequency of injections depend on the severity of the deficiency, with initial treatments often requiring multiple injections per week, followed by monthly maintenance doses. Results can be seen within days to weeks, depending on the individual and the severity of the deficiency.
Conclusion
When comparing sublingual B12 supplementation and B12 injections, the choice ultimately depends on the individual's needs, preferences, and the severity of the deficiency- and of course, what the individual's doctor recommends.
Sublingual supplements are non-invasive not to mention effective, convenient, and inexpensive. We recommend the Why Not Natural methylcobalamin B12 which is a pure, 3rd party tested, effective B12 supplement and a 60-day supply often costs less than a single injection.
Don't forget to subscribe to our newsletter to learn which supplements to take, how to combine them for maximum benefit, and other health tips to boost your energy and vitality. Plus, discover natural strategies to reduce hormonal imbalances, stress, and anxiety. Click here to get started!
References
(1) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30632091/
