

· By Lorea Lastiri
Are Vitamin D Supplements Effective? (Answered!)
Vitamin D supplements get a lot of attention — and for good reason. They play a key role in keeping your bones strong, muscles moving, nerves communicating, and immune system working properly. Vitamin D also helps your body absorb calcium and supports protection against infections and chronic illnesses.
If you’re dealing with muscle weakness, immune challenges, or conditions like sclerosis — or you simply want to support healthy bones and overall wellness — Vitamin D is one of the most reliable nutrients to pay attention to.
This guide walks through what vitamin D does, how to spot deficiency, who may need supplements the most, and how effective they really are.
What Is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is an essential fat-soluble nutrient your body converts into a hormone. Its main jobs include helping you absorb calcium and phosphorus — two minerals crucial for strong bones and healthy muscles.
You make it naturally when sunlight hits your skin, but you can also get smaller amounts from certain foods or supplements.
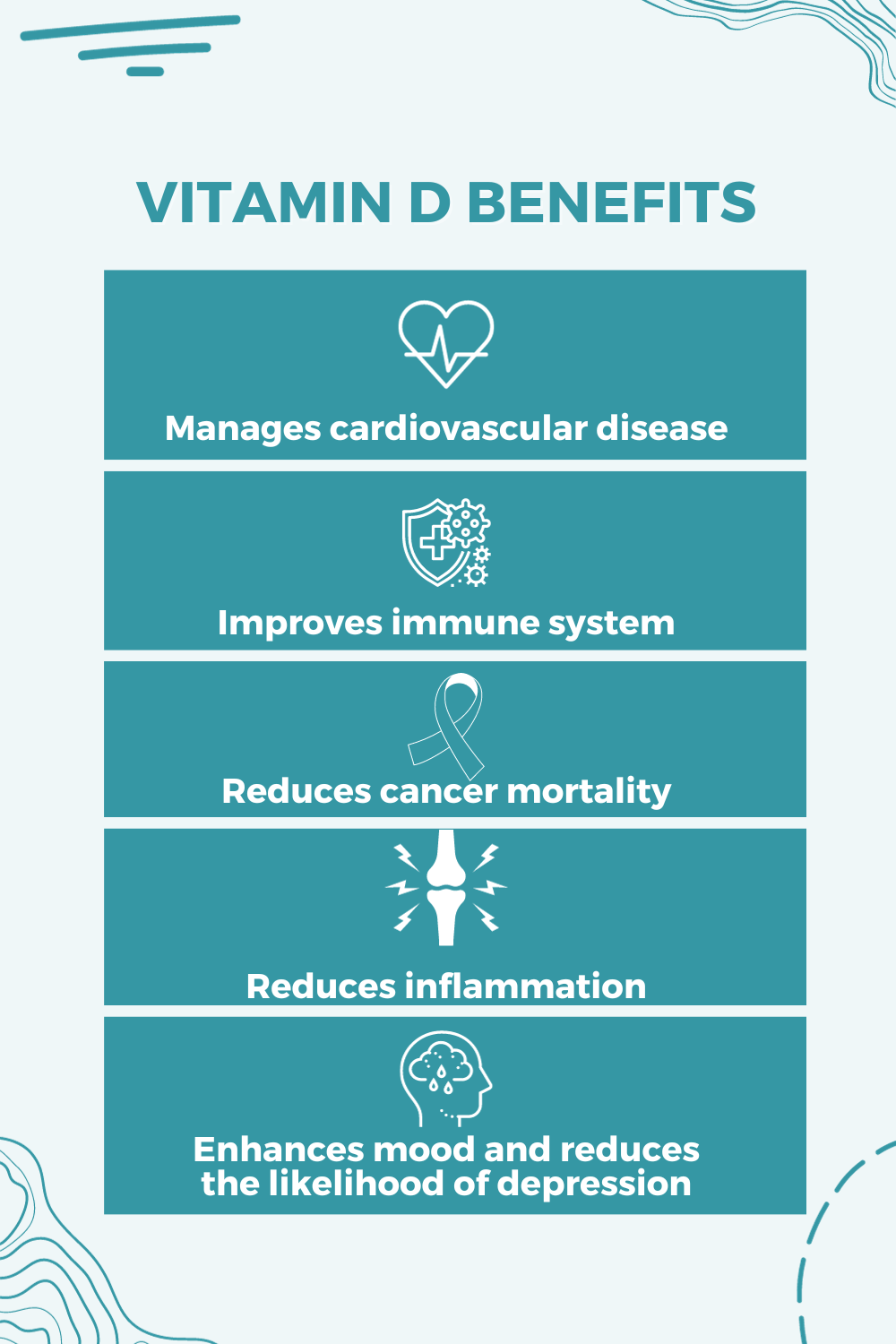
Some widely observed benefits include:
-
Supporting cardiovascular health
-
Strengthening immune function
-
Helping reduce inflammation
-
Supporting mood balance
-
Lowering mortality in certain cancers (not risk — mortality)

Common Sources of Vitamin D
The sun is your most powerful natural source of vitamin D. Your body also gets smaller amounts from foods like:
-
Fatty fish
-
Fish liver oils
-
Egg yolks
-
Beef liver
-
Fortified foods (milks, plant milks, cereals, orange juice)
-
UV-exposed mushrooms
-
Cod liver oil
Because very few foods naturally contain enough vitamin D, most people rely on fortified foods or supplements to reach healthy levels.
What Is Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency happens when your body doesn’t get enough sunlight, food, or supplementation to maintain healthy levels.
Severe deficiency is linked to bone-related conditions like osteoporosis and fractures. Mild deficiency can show up as:
-
Muscle weakness
-
Fatigue
-
Bone or back pain
-
Fragile bones in older adults
-
Joint stiffness
-
Muscle twitching
-
Mood imbalance
-
Anxiety
-
Hair loss
It’s especially common in people with darker skin, limited sun exposure, or people over 65 (their kidneys don’t convert vitamin D as efficiently).
Why Some People May Need a Vitamin D Supplement
Food sources alone rarely provide enough vitamin D — and unless you live a sun-kissed, beach-bum lifestyle year-round, sunlight isn’t always reliable either.
Some challenges:
-
You’d need to drink about five full glasses of milk to hit your daily recommended amount.
-
Indoor jobs and remote work often limit sunlight exposure.
-
Sunscreen (which is necessary!) also reduces vitamin D synthesis.
That’s why supplements are a practical way to maintain healthy levels without relying on circumstances you can’t control.
What Groups Are More Likely to Need Vitamin D Supplements?
1. Lactose-Intolerant People
Since many fortified products contain dairy, people avoiding lactose often miss out on one of the easiest sources of vitamin D. Supplements help fill the gap.
2. Breast-Fed Infants
Breast milk is wonderful — but it contains almost no vitamin D.
Most infants need around 400 IU per day unless they already take a multivitamin that includes vitamin D.
3. People With Limited Sun Exposure
If you work indoors, live in a northern climate (like New York), or cover much of your skin for cultural or personal reasons, you may naturally fall short on vitamin D.
Sun-poor environments also correlate with seasonal mood challenges.
4. People With Bone Diseases
Conditions like osteoporosis or Paget’s disease often require higher vitamin D intake, typically paired with calcium.
5. People With Obesity
Vitamin D can get trapped in fat cells, making it harder for the body to use. Those with a BMI above 30 may need more vitamin D to compensate.
6. Children With Rickets
Rickets — though rare — occurs when children have severely low vitamin D levels.
It’s more common in African-American children and may cause:
-
Bone pain
-
Weakness
-
Bowed legs
-
Joint deformities
Supplementation is the primary treatment.
7. People With Kidney or Liver Disease
These organs activate vitamin D. If they can’t convert it properly, supplements (often in active forms) become necessary.
8. Vegans
Vitamin D levels tend to run lower in vegans since most natural sources are animal-based.
Many plant milks are now fortified, but when diet alone isn’t enough, supplements help maintain normal D3 levels.
9. People Who Have Had Weight-Loss Surgery
Procedures like gastric bypass reduce absorption.
Healthcare providers often monitor vitamin D levels and recommend supplements if levels drop.
Other groups who may also need additional vitamin D include:
-
Pregnant people with low levels
-
People with fat-absorption issues
-
Those with cystic fibrosis, Crohn’s, or similar conditions
-
People who are very dark-skinned
-
Individuals with certain lymphomas
What Are the Recommended Vitamin D Intakes?
General guidelines:
-
Adults: 600 IU daily
-
Adults 70+: 800 IU daily
-
Infants (0–1 year): 400 IU daily
However, many adults need 3,800–5,000 IU to reach optimal blood levels based on recent studies.
Patients recovering from long hospital stays may require temporarily higher amounts under medical supervision.
Health Risks From Excessive Vitamin D Intake
You can get too much — but it’s rare.
Vitamin D toxicity (hypercalcemia) happens when people take more than 10,000 IU daily for extended periods.
Symptoms may include:
-
Loss of appetite
-
Vomiting
-
Metallic taste
-
Digestive issues
Always follow dosage guidance and talk to your doctor when using high-dose supplements.
How Effective Are Vitamin D Supplements?
Very effective — especially for people who can’t get enough sunlight or dietary sources.
Vitamin D:
-
Is natural
-
Has no side effects at normal doses
-
Is easy for the body to store and use over time
For best results, daily supplementation is ideal, though some people use weekly or monthly high-dose prescriptions.
There are two forms:
-
Vitamin D2: Plant-based
-
Vitamin D3: The form your body naturally produces — and typically more effective
Most experts recommend D3.

The Latest Research on Vitamin D Supplements
Recent high-quality studies show:
-
Vitamin D supplementation helps manage low bone mass, osteoporosis, and deficiency.
-
It does not significantly reduce fracture risk or heart disease in healthy individuals.
-
For cancer patients, supplementation may reduce mortality (not cancer risk).
-
The effectiveness varies depending on the individual's health conditions and baseline vitamin D levels.

Takeaway: Choose the Best Vitamin D Supplement
Vitamin D is essential, widely deficient, and extremely easy to fix with a high-quality supplement.
Whether you’re addressing low levels, supporting your bones, or simply navigating a lifestyle without much sunlight — supplements are a reliable, effective way to maintain healthy vitamin D status.
Our Vitamin D3-K2 capsules have 110,000 IU of D3 per capsule, which is excellent for people who need to get their vitamin D concentration level higher as fast as possible. They also contain US grown Spirulina with no fillers. Find it here!
✨ Subscribe for More Wellness Tips
Want easy, science-backed health tips in your inbox? Join our newsletter and get the latest on supplements, nutrition, and healthy living.
https://whynotnatural.com/pages/subscribe
Disclaimer
This content is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always speak with your healthcare provider before starting new supplements or making changes to your routine.
